Thunderbolt interface has been gradually used in notebook computers, desktop computers, docking stations, displays, memory and other devices. Thunderbolt has always been popular among consumers because of its powerful functions and its ability to realize data transmission, power transmission, audio and video transmission and other functions with a simple cable connection. In response to market development, Intel also officially released Thunderbolt 5 in September 2023, and demonstrated prototypes of laptops and docking stations that support Thunderbolt 5.
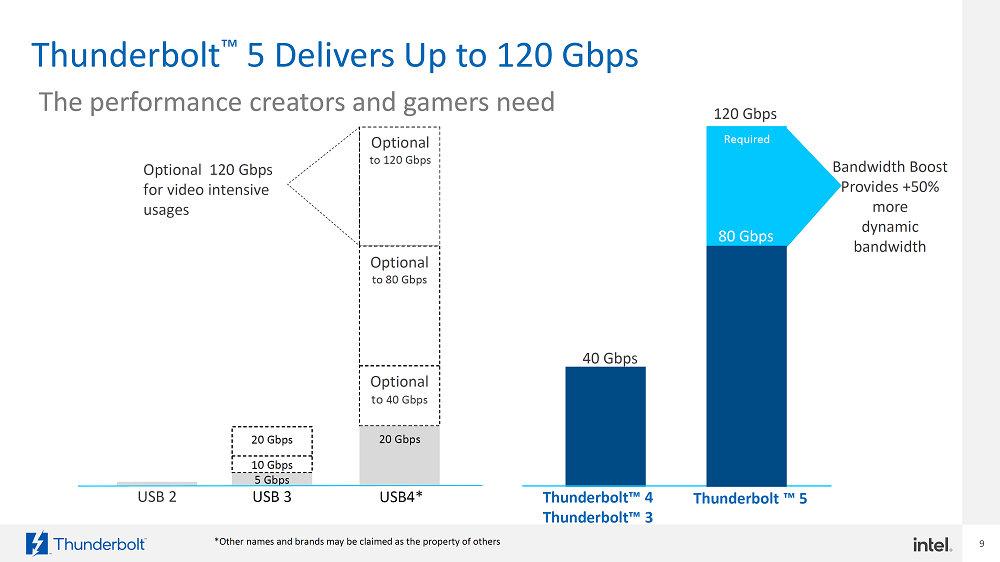
The design of Thunderbolt 5 is based on the complete version of the USB4 V2 specification. The rate can reach 80Gbps in conventional symmetrical transmission mode. At the same time, it can also provide transmission speeds of up to 120Gbps (120Gbps transmission, 40Gbps reception) in asymmetric transmission mode. Compared with Thunderbolt 4, the transmission bandwidth is increased by 3 times, and the power supply wattage can reach 240W. The powerful functions of Thunderbolt 5 can not only meet the needs of general users in usage scenarios, but also meet the ultra-high demand for high-resolution displays from professional users such as gamers and video makers.

Caption: Thunderbolt 5 will use new logos for brand and cable identification
(From GRL)

Source: Apple.com
Thunderbolt 2 was launched in June 2013. Intel released the second-generation Thunderbolt controller "Falcon Ridge" and named this interface product Thunderbolt 2 (still using the Mini DisplayPort interface). Compared with Thunderbolt 1, its transmission speed is doubled. to 20Gbit/s (bidirectional transmission), and can also transmit 4K resolution displays.
Starting from Thunderbolt 3, Intel has opened its technology to the outside world, that is, the related technology licensing fees have been converted into a reduced form (but manufacturers still need to pay for certification, which is different), and the 10th generation Core Ice Lake processor has integrated Thunderbolt 3 controller Inside the CPU, this time also means that the cost of using the interface has been significantly reduced compared to the previous two generations. Thunderbolt 3 has begun to use the USB-C interface, and the bandwidth has been upgraded to 40Gbit/s, enabling one interface to complete multiple functions and complete the integration of multiple ecosystems. Whether it is audio and video transmission, data transmission, or fast charging, it can all be achieved through Thunderbolt 3.
Thunderbolt 4 is based on the Thunderbolt 3 architecture and was launched in 2020. In the same year, Intel launched a mobile PC processor code-named "Tiger Lake", which was the first processor to integrate Thunderbolt 4. In terms of interface type and bandwidth, Thunderbolt 4 does not seem to be much different from Thunderbolt 3. However, as the latest generation of Thunderbolt technology, it not only supports the new USB4™, DisplayPort 1.4 and PCIe 3.0x4 (not less than 32Gbps) , and the user context has also been greatly expanded.
Thunderbolt 5 technology is expected to be first provided through the Barlow Ridge independent chip method in 2024, returning to the earlier Thunderbolt technology model that requires adding an additional chip to the existing platform. It can be used with PCs or laptops, and there are also a growing number of peripheral devices. into the design output.
(From GRL)
Short story: In 2019, Intel announced that it would contribute the Thunderbolt 3 protocol to the USB Promotor Group, allowing the Thunderbolt 3 protocol to be integrated into the new USB4 architecture.
Thunderbolt certification requirements include Pre-Cert, electrical performance testing (EV; Electrical Validation) and functional testing (FV; Functional Validation).
Intel also announced the Thunderbolt Host FV certification specification Version 2.0 in the Q4 stage of 2023, in which the following test items have been added to the verification of Thunderbolt 5 laptops and external devices:
(From GRL)
In the future, Thunderbolt 5 is expected to revolutionize connectivity and data transmission, catering to the increasingly demanding needs of both general and professional users. It promises to offer enhanced compatibility, improved performance, and expanded capabilities, setting a new standard for high-speed connectivity in various devices and applications.
The design of Thunderbolt 5 is based on the complete version of the USB4 V2 specification. The rate can reach 80Gbps in conventional symmetrical transmission mode. At the same time, it can also provide transmission speeds of up to 120Gbps (120Gbps transmission, 40Gbps reception) in asymmetric transmission mode. Compared with Thunderbolt 4, the transmission bandwidth is increased by 3 times, and the power supply wattage can reach 240W. The powerful functions of Thunderbolt 5 can not only meet the needs of general users in usage scenarios, but also meet the ultra-high demand for high-resolution displays from professional users such as gamers and video makers.
Caption: Thunderbolt 5 will use new logos for brand and cable identification
What is the difference between Thunderbolt 5 and Thunderbolt 4?
Support Bandwidth
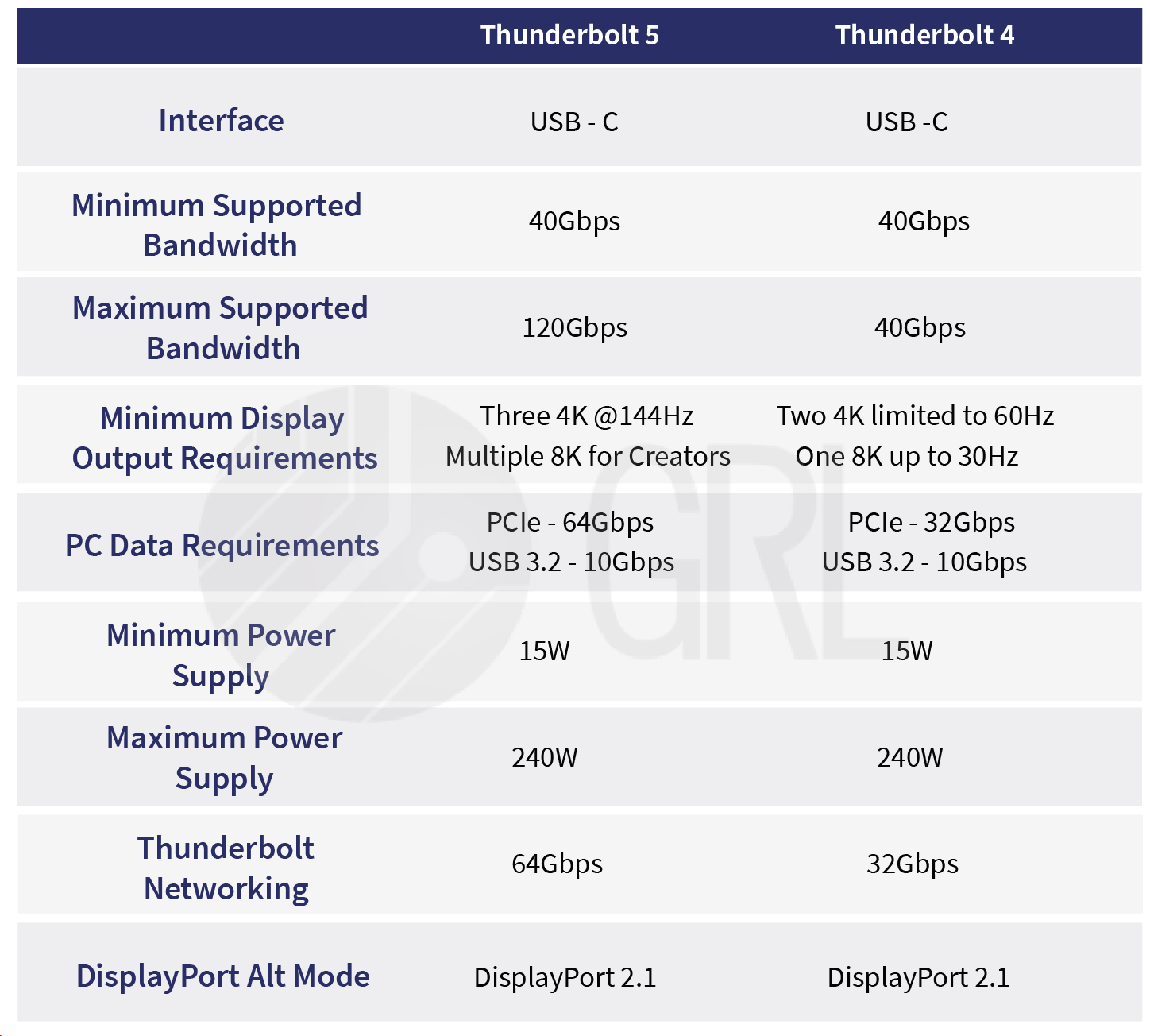
Thunderbolt 5's PCIe is Gen4, and its transmission bandwidth is twice that of Thunderbolt 4. It can be efficiently used in storage devices and external graphics cards.Networking Speed
Thunderbolt networking can use a Thunderbolt data line between two laptops for point-to-point connection to achieve data transmission. The transmission function of Thunderbolt 5 Networking is twice that of Thunderbolt 4 Networking. A single cable can realize instant file transfer from laptop to laptop.Signal Encoding
The electrical layer of Thunderbolt 5 is the same as USB4 Gen4, using PAM3 (Pulse Amplitude Modulation 3-level) signal encoding (; while Thunderbolt 4 uses NRZ signal encoding. Considering the total loss and bit error rate, PAM-3 Both are better than NRZ, which can significantly reduce signal losses in chips, chip packages, circuit boards, connectors and cables, improving Thunderbolt transmission performance.Support Screen
Thunderbolt 5 can display 540Hz in Full HD mode, supports 8K screens, or can be connected to three external 4K 144Hz screens; Thunderbolt 4 can be connected to two external 4K 60Hz screens or one 8K 30Hz screen.Thunderbolt 5 backwards compatible
Thunderbolt 5 supports USB4 V2, PCle Gen 4, DisplayPort 2.1, is compatible with Thunderbolt 3 and 4, etc.(From GRL)
The evolution of Thunderbolt™
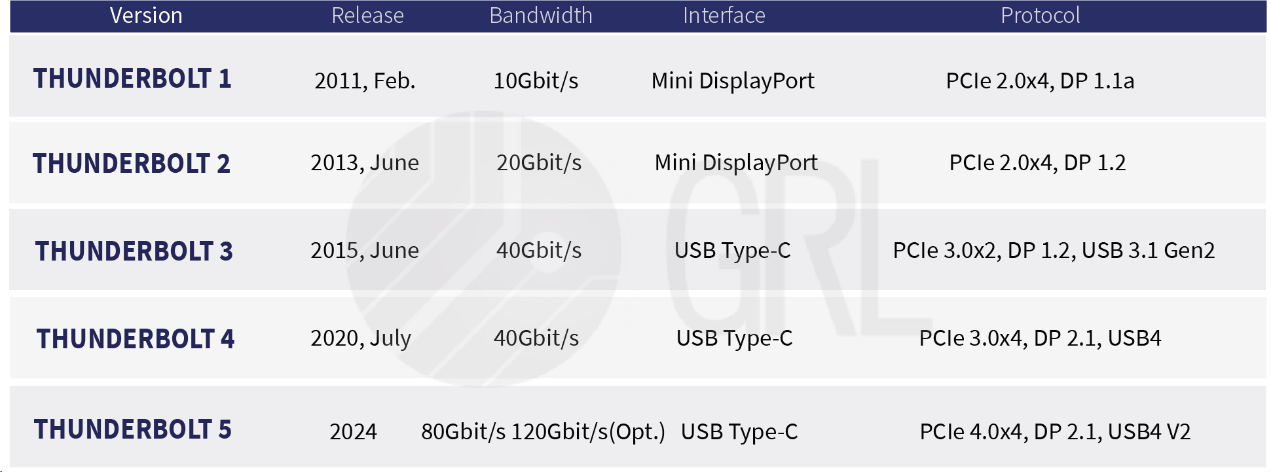
Intel has been promoting Thunderbolt, which has actively participated in the development of Apple since 2011. In the same year, Apple launched a new MacBook Pro product line and announced the adoption of a new generation I/O interface, integrated with Mini DisplayPort, which can be used through Daisy-chain Connect up to 6 peripheral devices. At this time, Thunderbolt is officially launched on the market, and its two-way transmission speed can reach 10Gbit/s.Source: Apple.com
Thunderbolt 2 was launched in June 2013. Intel released the second-generation Thunderbolt controller "Falcon Ridge" and named this interface product Thunderbolt 2 (still using the Mini DisplayPort interface). Compared with Thunderbolt 1, its transmission speed is doubled. to 20Gbit/s (bidirectional transmission), and can also transmit 4K resolution displays.
Starting from Thunderbolt 3, Intel has opened its technology to the outside world, that is, the related technology licensing fees have been converted into a reduced form (but manufacturers still need to pay for certification, which is different), and the 10th generation Core Ice Lake processor has integrated Thunderbolt 3 controller Inside the CPU, this time also means that the cost of using the interface has been significantly reduced compared to the previous two generations. Thunderbolt 3 has begun to use the USB-C interface, and the bandwidth has been upgraded to 40Gbit/s, enabling one interface to complete multiple functions and complete the integration of multiple ecosystems. Whether it is audio and video transmission, data transmission, or fast charging, it can all be achieved through Thunderbolt 3.
Thunderbolt 4 is based on the Thunderbolt 3 architecture and was launched in 2020. In the same year, Intel launched a mobile PC processor code-named "Tiger Lake", which was the first processor to integrate Thunderbolt 4. In terms of interface type and bandwidth, Thunderbolt 4 does not seem to be much different from Thunderbolt 3. However, as the latest generation of Thunderbolt technology, it not only supports the new USB4™, DisplayPort 1.4 and PCIe 3.0x4 (not less than 32Gbps) , and the user context has also been greatly expanded.
Thunderbolt 5 technology is expected to be first provided through the Barlow Ridge independent chip method in 2024, returning to the earlier Thunderbolt technology model that requires adding an additional chip to the existing platform. It can be used with PCs or laptops, and there are also a growing number of peripheral devices. into the design output.
(From GRL)
Short story: In 2019, Intel announced that it would contribute the Thunderbolt 3 protocol to the USB Promotor Group, allowing the Thunderbolt 3 protocol to be integrated into the new USB4 architecture.
Compulsory certification through mark recognition technology
Starting from Thunderbolt 3, the USB Type-C interface has been used, which has made the application range wider and more diverse, providing end consumers with greater flexibility and more functional uses, but it has also made the product more complex in terms of design and old technology. Downward compatibility is required. If there are factors such as poor protocol communication between products, it is easy to cause mutual incompatibility between ecosystems, which will ultimately lead to the product not functioning properly and the user experience being poor. In order to ensure Thunderbolt user experience and product quality, Intel emphasizes that if manufacturers want to use the Thunderbolt logo or icon, they must pass Thunderbolt certification testing and sign a Thunderbolt trademark license.Thunderbolt certification requirements include Pre-Cert, electrical performance testing (EV; Electrical Validation) and functional testing (FV; Functional Validation).
Intel also announced the Thunderbolt Host FV certification specification Version 2.0 in the Q4 stage of 2023, in which the following test items have been added to the verification of Thunderbolt 5 laptops and external devices:
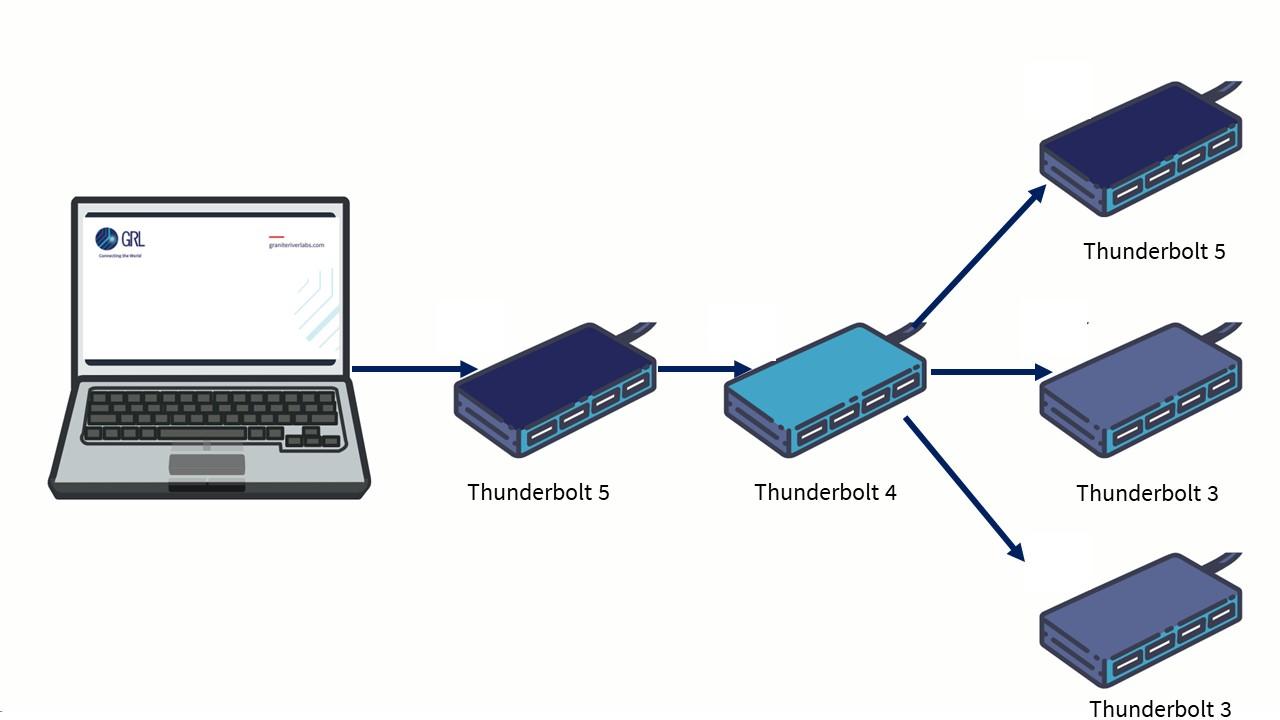
- 3.2.1 Hot Plug/Unplug (New link method: Host 🡨 🡪TBT5 🡨🡪TBT4🡨🡪TBT3)
- 3.2.2 Power Cycle/Reboot (New connection method: Host 🡨 🡪TBT5 🡨🡪TBT4🡨🡪TBT3)
- 3.2.4 Sx Flow (new connection method: Host 🡨 🡪TBT5 🡨🡪TBT4🡨🡪TBT3)
- 3.2.5 Peer to Peer (Added TBT5 laptop for Peer to Peer data transmission)
- 3.4.4 Complex Topology (new connection method as shown below)
- 3.4.5 Performance (new Thunderbolt 5 storage class device)
(From GRL)
Conclusion
The Thunderbolt interface, known for its powerful functions and simple cable connectivity, saw a significant advancement with the release of Thunderbolt 5 by Intel in September 2023. Based on the USB4 V2 specification, Thunderbolt 5 offers increased transmission bandwidth, higher power supply wattage, and improved networking speed and signal encoding compared to Thunderbolt 4. It supports USB4 V2, PCle Gen 4, DisplayPort 2.1, and is backward compatible with Thunderbolt 3 and 4. Looking ahead, Thunderbolt 5 is expected to provide enhanced connectivity and data transmission capabilities, catering to the needs of both general and professional users.In the future, Thunderbolt 5 is expected to revolutionize connectivity and data transmission, catering to the increasingly demanding needs of both general and professional users. It promises to offer enhanced compatibility, improved performance, and expanded capabilities, setting a new standard for high-speed connectivity in various devices and applications.

